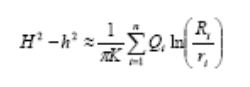Restricted aquifer (constrained aquifer steady state convergence flows to a well)
The pressure head surface of the aquifer sinks with the well as the center, which is called the drawdown curve or cone of depression; R is called the radius of influence. If the aquifer is homogeneous and isotropic, the stable radial flow Q at the position r from the center of the well is
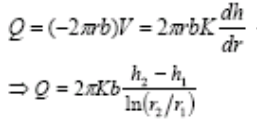
In the formula K is hydraulic conductivity (hydraulic conductivity), or known as permeability (permeability). h1 and h2 are the water levels of observation well 1 and observation well 1, respectively, r1 and r2 are the distances from the center of observation well 1 and observation well 1 respectively, and b is the thickness of the aquifer Unrestricted aquifer (steady convergent flow of free aquifer to a well) The pumping capacity in the homogeneous and isotropic unrestricted aquifer is
If there is observation well data, you can get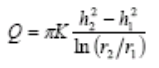
Compound well flow field (limited aquifer)
In restricted aquifers
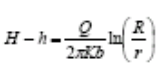
Therefore, the pressure relief of the simultaneous pumping of multiple wells can be expressed as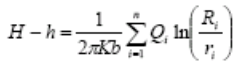
Compound well flow field (unrestricted aquifer)
Define water surface discharge sw = H − hw, when sw << H
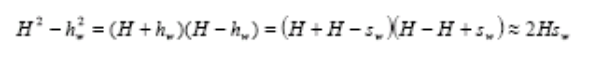
Since the water level H of the steady aquifer can be regarded as a fixed value, 2Hsw can still be regarded as linear. Therefore, the problem of simultaneous pumping of multiple wells in unrestricted aquifers can be treated in a linear superposition method as follows
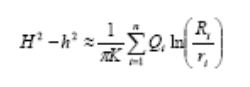
The pressure head surface of the aquifer sinks with the well as the center, which is called the drawdown curve or cone of depression; R is called the radius of influence. If the aquifer is homogeneous and isotropic, the stable radial flow Q at the position r from the center of the well is
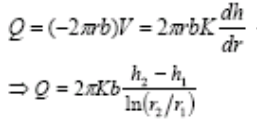
In the formula K is hydraulic conductivity (hydraulic conductivity), or known as permeability (permeability). h1 and h2 are the water levels of observation well 1 and observation well 1, respectively, r1 and r2 are the distances from the center of observation well 1 and observation well 1 respectively, and b is the thickness of the aquifer Unrestricted aquifer (steady convergent flow of free aquifer to a well) The pumping capacity in the homogeneous and isotropic unrestricted aquifer is

If there is observation well data, you can get
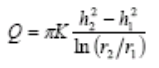
Compound well flow field (limited aquifer)
In restricted aquifers
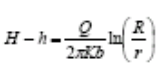
Therefore, the pressure relief of the simultaneous pumping of multiple wells can be expressed as
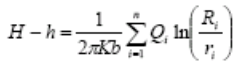
Compound well flow field (unrestricted aquifer)
Define water surface discharge sw = H − hw, when sw << H
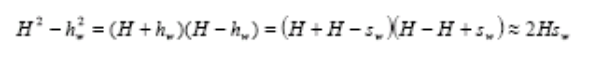
Since the water level H of the steady aquifer can be regarded as a fixed value, 2Hsw can still be regarded as linear. Therefore, the problem of simultaneous pumping of multiple wells in unrestricted aquifers can be treated in a linear superposition method as follows