The topography of Yunlin County is narrow and long, irregularly rectangular, and the eastern part is the Yushan Mountains of the Central Mountain Range. The terrain is gradually flattened, and the area of mountains over 1,000 meters is limited. More than 87% of the county's area is flat plain terrain, only Douliu City and Linnei Township are mountain hills, and Gukeng Township is a terrain between mountain hills and middle and high altitudes. The geological structure of Yunlin County can be divided into Miocene to Pleistocene rock layers, platform gravel layers and alluvial layers. It belongs to the geological area of the foothill belt of western Taiwan. It is mainly composed of tertiary crushed rock layers, and the main rocks are interlayers of sandstone and shale. It is composed of convex mirror body or thin layer with limestone and tuff partially interposed. The vast majority of the county boundary is a modern alluvial layer, mainly composed of clay, silt, sand and gravel, widely covering the plain and basin area.
According to the results of the "Taiwan Area Groundwater Observation Network Overall Plan" compiled "Taiwan Area Groundwater-Zhuoshui Stream Alluvial Fans" report, the Yunlin Plain Hydrogeological Survey the location of various quality drilling sites and 5 sets of stratum profiles are shown in Figure 3 -2.1. According to the core records of each section, it can explain the thickness and extension of different sediments in the underground strata. The geological characteristics of each section are described as follows:
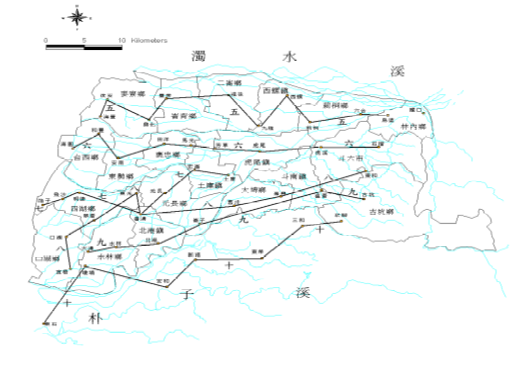
3-2.1 Distribution map of hydrogeological profiles in Yunlin area (profiles 5 to 10))
1. Haifeng-Wutu section (with figure 3-2.2) There are 10 drilling points in this profile, most of the east of Xiluo is thick gravel, and even a thin layer of mud layer, except for the surface of Liutong to Liuhe, it is covered with a thick mud layer of about 5 to 15 meters, which affects the rainfall infiltration In addition, the rest have a good infiltration mechanism; after the Xiluo arrives at the port, it is interbedded with gravel and medium coarse sand, and occasionally contains a thin layer of mud, but because the surface between Jiulong and the back of the port is covered by a layer of mud about 5 meters thick And there is a water blocking layer about 5 to 10 meters thick under the surface of the section, making it difficult for rainwater to directly infiltrate into the main aquifer; after the port to Haifeng, except for the mud layer about 5 meters thick near the surface, the surface The main part is composed of very fine sand and mud layer with poor water conductivity.
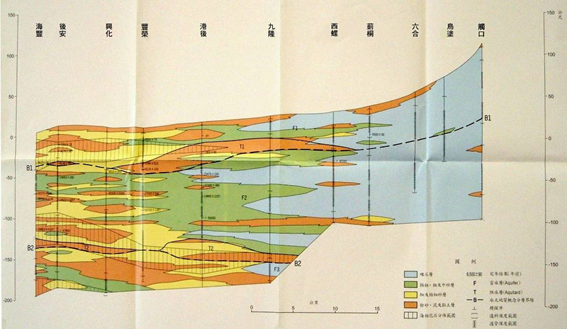
Source: Central Geological Survey, Ministry of Economic Affairs,1999
Figure 3-2.2 Hydrogeological section of the “Haifeng-Wutu” section in the Yunlin area
2. Haiyuan-Pomegranate section (with figure 3-2.3) There are 10 drilling points in this profile. Huwei to Pomegranate are composed of thick gravel layers and coarse sand. Even thin layers of mud are interposed. Infiltrate. Fangcao to Annan is composed of coarse, medium and fine sand and mud layers. Although the coarse and medium sand layers form a groundwater circulation channel, the fine sand and mud layers between Fangcao and Haiyuan are very thick and continuous. Extensive water blocking layer.
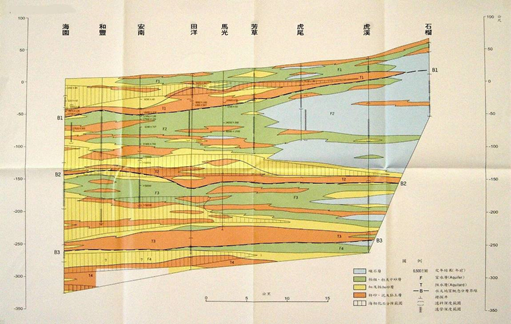
Source: Central Geological Survey, Ministry of Economic Affairs, 1999
Figure 3-2.3 Hydrogeological section of the "Haiyuan-Pomegranate" section in the Yunlin area
3. Bozi-Tuku section (Figure 3-2.4) There are 7 drilling points in this profile. There is a continuous mud layer about 5 to 20 meters thick between 20 and 60 meters below the surface, which constitutes the water blocking layer in this area. The thick gravel layer, coarse sand layer and Honglun have thick thick and medium sand layers. Most of the rest are composed of fine sand with poor water conductivity.
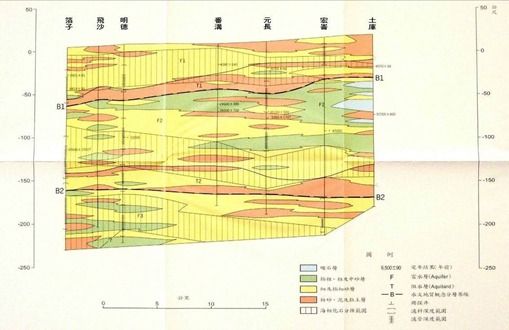
Source: Central Geological Survey, Ministry of Economic Affairs, 1999
Figure 3-2.4 Hydrogeological section of the “Bozi-Tuku” section in the Yunlin area
4. Yiwu-Donghe section (with photos 3-2.5) There are 8 drilling points in this profile. To the east of Fangou, it is composed of gravel layer and coarse sand layer, with thin layer of mud layer and fine sand layer in between; to the east of Fangou is mostly fine sand layer interlaced mud layer and thin coarse sand layer. composition. Except for Jiaxing, Fangou and Kouhu which have mud layers about 5 to 10 meters thick near the surface, the rest can allow rainwater to infiltrate directly into the shallow aquifer.
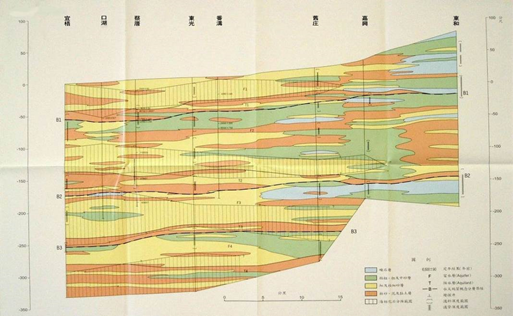
Source: Central Geological Survey, Ministry of Economic Affairs, 1999
Figure 3-2.5 Hydrogeological section of "Yiwu-Donghe" section in Yunlin area
5. Dagou-Gukeng section (with figure 3-2.6)
There are 6 drilling points in this profile. The east of Beigang is composed of gravel layer and coarse and medium sand layer from Wencuo to Gukeng, and the coarse, medium and fine sand layer is between Beigang and Wencuo, with mud layer in between. And there is no mud layer covering the surface from Beigang to Gukeng, but a mud layer about 15 to 25 meters thick blocks the groundwater of the shallow aquifer from about 20 to 50 meters below sea level between Beigang and Wencuo. Infiltration; west of Beigang, except for about 50 to 80 meters below sea level, which is composed of coarse and medium sand layers, the rest is mostly composed of fine sand layers and mud layers, and there is mud about 5 to 10 meters thick on the surface covered with layers to block rainwater infiltration.
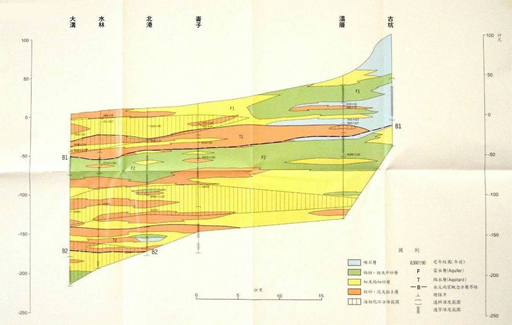
Source: Central Geological Survey, Ministry of Economic Affairs, 1999
Figure 3-2.6 Hydrogeological section of the "Dagou-Gukeng" section in the Yunlin area
According to the above-mentioned hydrogeological survey of Yunlin area, the quality drilling data (Table 5-1.9) mainly consist of clay and sand, and the proportion of clay exceeds 40%, indicating that it has a high compression potential. The distribution of geological characteristics in the forest area (Figure 5-1.4) also shows that the areas with high clay and sand content are mainly concentrated in the fan center and fan tail area.
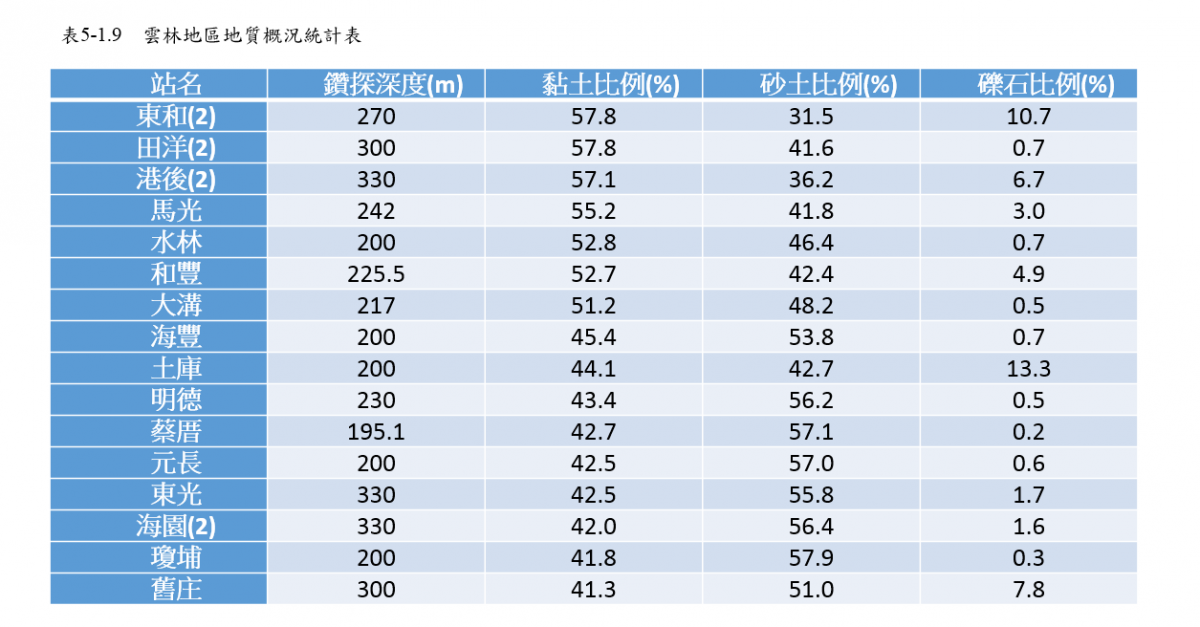
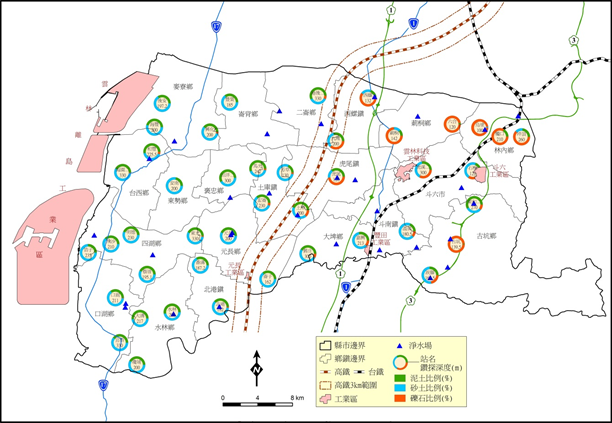
Figure 5-1.4 Distribution of geological characteristics in Yunlin area
References: 1. "Compilation of the results of the overall plan of Taiwan's groundwater observation network (1992-2008)"
2. "Taiwan Region Hydrogeological Zoning Characteristics", Central Geological Survey, 2008.
3. Monitoring and analysis of formation subsidence in Taipei, Chiayi, Kaohsiung and Pingtung in 2015
4. In 2014, diversified monitoring and integration technologies were applied to strata subsidence monitoring in Taipei, Changhua and Yunlin



