The first phase of the Taiwan Groundwater Observation Network from 1992 to 1998, the Central Geological Survey of the Ministry of Economics completed 52 hydrogeological drills in the Pingtung Plain. The hydrogeological stratification within a depth of about 220 meters in the Pingtung Plain can be divided from top to bottom There are seven layers: aquifer 1, aquiclude 1, aquifer 2, aquiclude 2, aquifer 3-1, aquiclude 3, and aquifer 3-2.n the "Phase 1 Project of Taiwan Groundwater Observation Network-Pingtung Plain Hydrogeological Survey and Research Report" completed by the Central Geological Survey of the Ministry of Economic Affairs, a total of 13 hydrogeological profile lines were built in the Pingtung Plain (Figure 4-1.49 ), it can be seen from the geological section that the aquifer in the Pingtung Plain is extremely developed, with a large thickness and spreading throughout the whole area, and the top layer of gravel near the surface unconfined aquifer becomes thinner towards the west.aquiclude only has a relatively continuous distribution in the coastal area and is sandwiched by the aquifer, and its thickness is much smaller than that of the aquifer. Therefore, the aquifer is only significantly separated on the south side, and it is unified on the north and east sides of the plain. The following is a description of the changes in the lithology of the four aquifers as follows:
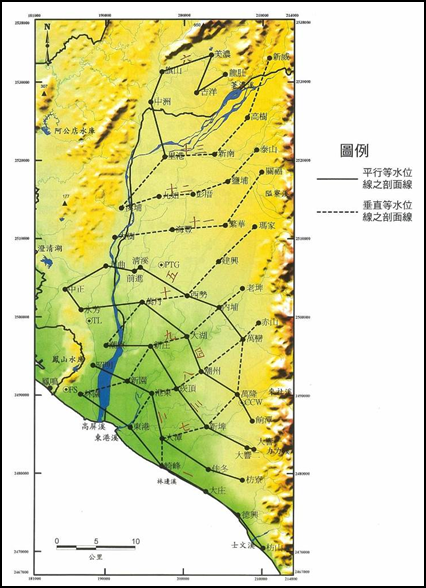
Source: The first phase of the Taiwan Groundwater Observation Network Project-Pingtung Plain Hydrogeological Survey and Research General Report.
Figure 4-1.49 Pingtung Plain Hydrogeological Section Distribution Map
1. Aquifer 1
Aquifer 1 is the surface layer of the aquifer system in the Pingtung Plain. The distribution range covers the whole area. The thickness ranges from 23.5 meters to 83.5 meters. The average thickness is about 49.9 meters. It is a free aquifer. The groundwater level is the deepest in the alluvial fan crest area under the Chaozhou fault, and the depth can reach about 45 meters. To the southwest, the water level gradually approaches the surface, and the closer is about a few meters below the surface. This floor is also a necessary place for replenishing underground water such as rainwater and river water.
2. Aquifer II
Aquifer 2 is located under Aquifer 1 and Water Barrier 1. The distribution range covers the whole area. Its depth is between 43 and 152 meters below the surface, and its thickness varies from 9 to 79.5 meters. The average thickness is about 51.5 meters. The lithology of this layer is the most developed with a gravel layer and good water discharge capacity. It forms the main layer of groundwater development in the Pingtung Plain with the aquifer one. The aquifer one is developed with shallow wells, and the depth of most deep wells reaches the aquifer two.
3. Aquifers three-one
Aquifer III is located under Aquifer II and Water Barrier II, the distribution range covers the whole area, its depth is between 95 and 210 meters below the surface, the thickness varies from 49.5 to 89 meters, and the average thickness is about 70.8 meters ruler. The lithology of this layer is most developed by the gravel layer. Because of the deeper depth, groundwater development is not as common as the aquifers one and two.
4. Aquifer three-two Aquifers three-two are located at the bottom of the aquifer system, and the distribution range covers the whole area. The depth of the top is 174-114 meters below the surface. The lithology of this layer is mainly gravel layer. The depth does not penetrate this layer, and its bottom position has not been determined. Due to the greater depth, there is less groundwater development.
According to the hydrogeological profiles of the Zhaoming to Fangliao section, Qifeng to Wanluan section, and Linyuan to Fanshan section (see Figure 4-1.50 to Figure 4-1.52), Pingtung area has good groundwater connectivity and aquifer thickness of about Between 100 meters and 200 meters. According to the geological section from Qifeng to Wanluan section, the water blocking layer is thin and broken, so the vertical infiltration replenishment effect in the upstream area is good.
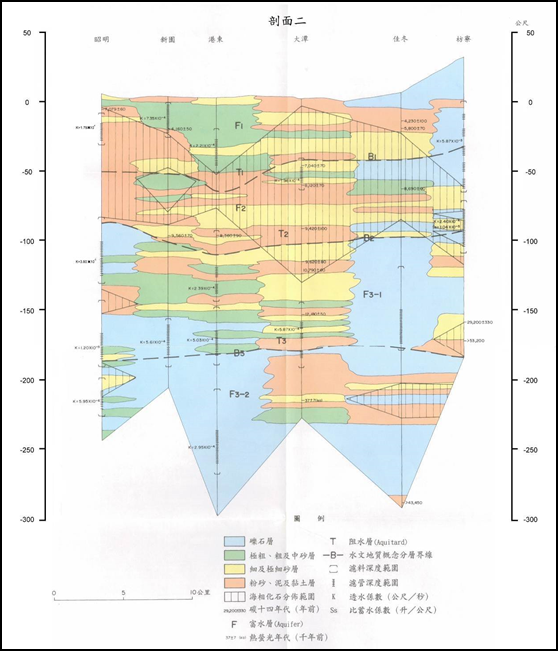
Source: The first phase of the Taiwan Groundwater Observation Network Project-Pingtung Plain Hydrogeological Survey and Research General Report.
Figure 4-1.50 Pingtung area "Zhaoming-Fangliao" hydrogeological section
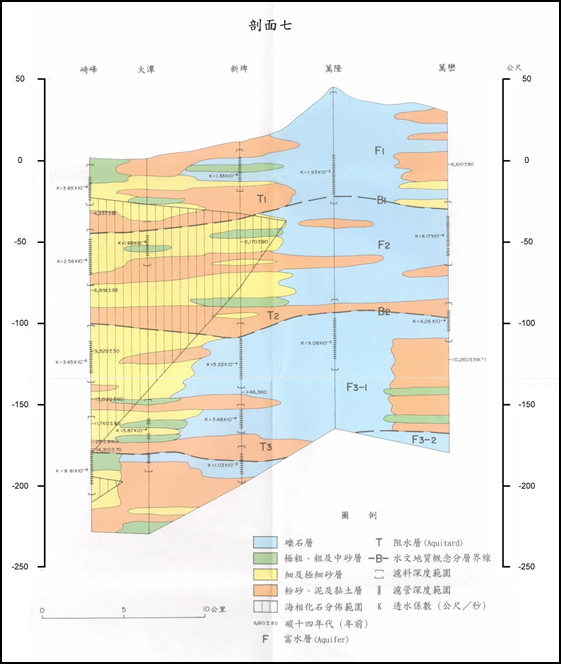
Source: The first phase of the Taiwan Groundwater Observation Network Project-Pingtung Plain Hydrogeological Survey and Research General Report.
Figure 4-1.51 Pingtung area "Qifeng-Wanluan" hydrogeological section
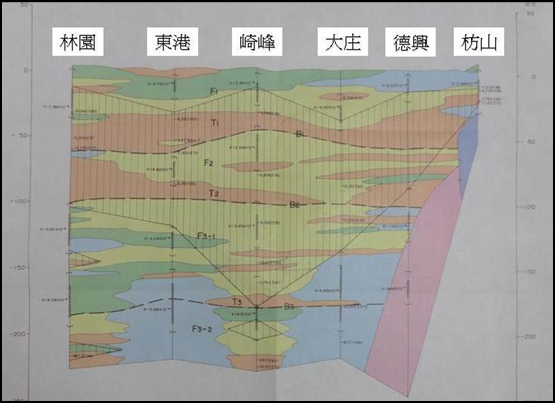
Source: The first phase of the Taiwan Groundwater Observation Network Project-Pingtung Plain Hydrogeological Survey and Research General Report.
Figure 4-1.52 "Geyuan-Fangshan" hydrogeological section of Pingtung area
According to the above-mentioned hydrogeological survey of the Pingtung subsidence area, the quality drilling data shows (Table 4-1.16 and Figure 4-1.53), mainly composed of sand and gravel (except for Qifeng and Jiadong Station, which contains more clay and sand Outside), and Jiadong Station has a relatively high clay percentage of about 57.8%.
.png)
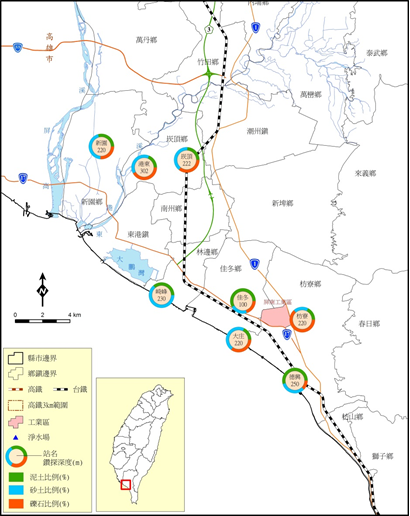
圖4-1.53 Figure 4-1.53 Pingtung area geological characteristics distribution
references:
1. "Compilation of the results of the overall plan for the groundwater observation network in Taiwan (1992-2008)"
2. "Taiwan Area Hydrogeological Zoning Characteristics", Central Geological Survey, 2008.
3. 2015 Subsidence Monitoring and Analysis of Taipei, Chiayi, Kaohsiung and Pingtung



